[ad_1]
Neil Thomas wished he may have been awake in the course of the operation to take away a 6cm cancerous tumour from his colon. He was one of many first individuals to go below the scalpel of College Hospital of Wales’s new robotic techniques in June 2022. And, because the founding father of a software program firm, the expertise him.
Thomas’s surgeon, James Ansell, would as soon as have stooped over his affected person’s physique to carry out the operation. As an alternative, he stood behind a console on one other aspect of the theatre carrying 3D glasses. His palms grasped two joysticks, which managed the 4 robotic arms that huddled round Thomas’s unconscious physique.
“My colleague mentioned to me the opposite day that this appears like dishonest,” Ansell says. “We’ve carried out it for thus a few years: stood on the bedside at an ungainly angle, sweating as a result of it’s actually bodily demanding surgical procedure. [Now,] sitting down, there’s no strain on the surgeon. It’s very easy.”
Robots have revolutionised the observe of surgical procedure since their introduction to working theatres in 2001. They’ll now be present in hospitals all internationally. Essentially the most prolific system, the Da Vinci, is utilized in 1.5m operations yearly, based on its California-based producer Intuitive Surgical.
Now, mixed with AI and different novel applied sciences, engineers are creating superior robotics to herald one other new period for surgical procedure – and this time, the surgeon’s position within the working theatre could change altogether.
Though robots are put to a wide range of duties in surgical procedure, their use as a device in performing laparoscopy – in any other case often known as keyhole surgical procedure – has attracted essentially the most consideration inside and outdoors drugs. Keyhole surgical procedure reduces the time sufferers must get better by working via smaller incisions. This subsequently reduces the possibility that sufferers catch infections, and so accelerates their recoveries.
With out robots, keyhole surgical procedure requires a really excessive stage of talent. Surgeons must function at awkward angles, transferring their palms in the wrong way to that by which they need their devices to maneuver contained in the physique. With robots, surgeons can carry out extra advanced operations which may in any other case have demanded open surgical procedure, they endure much less bodily pressure, and so they require much less coaching time. Furthermore, they’re getting higher at utilizing the robots.
“A few of these sufferers who’ve ultra-advanced illnesses involving blood vessels behind the pelvis would possibly nonetheless get an open operation,” says Deena Harji, a colorectal surgeon in Manchester, “however we’re beginning to see some very early case research popping out the place they’re beginning to have robotic approaches utilized to them, at the least partly. When robotics began 20 years in the past, that group wouldn’t have been eligible for robotic operation. However as we’ve got developed expertise and data, we are able to provide actually advanced sufferers robotic surgical procedure.”

Surgeons are restricted by their bodily capability, and their minds are restricted of their potential to be taught and enhance. That’s why engineers are hoping robotic techniques mixed with AI would possibly be capable of surpass the abilities of human surgeons to supply extra constant outcomes, with fewer errors.
Final 12 months, engineers at Johns Hopkins College within the US got here one step nearer to realising that aim. In what they described as probably the most delicate procedures within the observe of surgical procedure, their Good Tissue Autonomous Robotic (Star) sutured the ends of a severed gut collectively in 4 pigs – whereas they had been below anaesthetic. Based on the engineers, it carried out higher than a human surgeon would have. “Our findings present that we are able to automate probably the most intricate and delicate duties in surgical procedure,” Axel Krieger, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, and the mission’s director, mentioned on the time.
The Star’s process was not the primary time a robotic had carried out with a stage of autonomy in surgical procedure. The TSolution-One system (previously referred to as RoboDoc), for instance, is FDA-approved to arrange human limbs for joint replacements based on a surgeon’s plan. What makes the Star’s process particular was that it carried out its activity utilizing keyhole surgical procedure – a world first.
Surgical robotics presents an excellent alternative for engineers to introduce autonomy due to the huge quantity of knowledge that units can gather. An clever system, as soon as developed, can use this information to show itself. In concept, it may turn into higher with every operation that it performs because it gathers increasingly information. This might assist healthcare organisations “standardise” the outcomes of operations.
Mark Slack, the chief medical officer at CMR Surgical, which manufactures one other surgical robotic, Versius, says that producers have failed to take advantage of this information till now. That’s why they and researchers equivalent to these concerned within the Star mission are scrambling to gather and course of as a lot as attainable. “Information, information, information,” Slack says. “This information has had vital untapped potential.”
Regardless of the Star staff’s success, it’s nonetheless too early to forecast autonomous surgical procedure in hospitals any time quickly. Engineers discuss “ranges of autonomy”. For a robotic system, the query is just not whether or not it’s autonomous or not; the query is how autonomous it may be. And the Star system carried out solely a small part of a whole surgical procedure with out human assist. In actual fact, it even wanted people to use a fluorescent marker to information its actions. “You’re not presupposed to name it autonomous surgical procedure,” Tamás Haidegger, an affiliate professor of clever robotics at Óbuda College in Budapest, says. “That is automating one specific surgical subtask.”
Haidegger makes what he believes is one other vital distinction – between the form of complexity required for a system just like the Star and the units utilized in hospitals. Customary laboratory greatest observe in analysis environments typically falls in need of the security and design requirements of scientific settings, he says.
To be used in scientific environments, producers want to have the ability to clarify precisely how their units work, which continues to show a problem for individuals who develop AI. There’s additionally the approaching introduction of AI-specific regulation that governments internationally, together with the UK and EU, are creating. Autonomous surgical robots might want to adjust to these too.
Based on Haidegger, this all quantities to a really costly course of for producers to show that their units meet the regulatory necessities. Every system wants to achieve approval for every new discipline of surgical procedure, separately, which has already decelerated the adoption of the human-operated robots used immediately. It is going to take much more work for a business producer to determine that the potential revenue justifies the price of analysis and growth. “It’s not going to seriously change medical units in a single day,” Haidegger says.
Surgeons and engineers alike typically say that surgical robotics was born of a US navy ambition to carry out operations on injured frontline troopers with out inserting the surgeons in hurt’s manner. Many years later, healthcare networks are but to undertake telesurgery as a typical technique of observe. For analysis functions, nonetheless, it has been carried out. In 2001, for instance, a physician in New York operated on a affected person in France in what has turn into often known as the Lindbergh Operation. However such a process depends on a wired-line or equally sturdy connection – one which troopers would lack entry to on the battlefield. If the connection was misplaced, and even a lot as slowed down, the robotic would possibly hurt the affected person.
There may be some hope that quicker networks would possibly cut back this danger. And in 2019, a Chinese language hospital claimed to have efficiently carried out the world’s first telesurgical operation over a wi-fi 5G community. However based on Jin Kang, a professor {of electrical} and pc engineering at Johns Hopkins College, the pace or bandwidth of the community makes little distinction. “The communications, the web, the ability supply – many issues could possibly be unstable,” he says. “I believe that’s all the time a difficulty.”
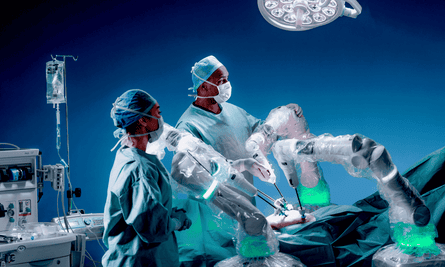
For now, it’s possible that technological progress within the working room will come within the type of minor enhancements to the prevailing mannequin of observe. Each Haidegger and Kang, who labored on the Star mission, imagine that machines will assist to enhance affected person outcomes within the shorter time period.
Present robots use cameras to supply surgeons with a 3D picture, which they will view via a headset or console. Newer units are enhancing that info with augmented actuality visuals. The most recent Da Vinci robots, for instance, provide a secondary “ultrasound” view. With AI, the robotic could even be capable of determine and spotlight vital info that the surgeon may need missed, as is already occurring in radiology.
For organisations with strict budgets, together with the NHS, the price of surgical robots has remained a prohibitive issue. The Da Vinci prices about £1.6m (the corporate wouldn’t verify a particular value, stating that it relies on the customer’s particular person necessities.) CMR Surgical’s Versius prices between £1.2 and £1.5m. This has modified little over the previous 20 years, and doesn’t embody the added price of coaching and upkeep, which could be 10% of the preliminary funding yearly.
Extra trusts are starting to purchase them although, with the assumption that the shorter restoration instances related to robotic surgical procedure can cut back general prices for hospitals. Jason Dorsett, chief finance officer at Oxford College Hospitals, says that this profit is especially pronounced for sufferers with head and neck cancers, who would possibly in any other case require lengthy post-operative hospital stays. The NHS’s well being economics unit is constant to guage this.
Whether or not they show cost-effective or not, surgeons agree that robotic techniques have made it simpler for them to carry out extra advanced procedures, whereas minimising scarring for his or her sufferers. Neil Thomas, the previous tech entrepreneur with a tumour that was faraway from his colon in June 2022, was capable of depart hospital solely two days after his operation.
Thomas had been coaching for an Ironman triathlon on the time of the prognosis. Three months after the operation (on physician’s orders), he was capable of return to coaching. First a one-mile run, after which just a few extra three days later. The robotic utilized in his operation had left solely a small assortment of virtually imperceptible scars throughout his stomach. “You’ll be able to’t see a factor,” he says. “And restoration, I assumed, was glorious.”
[ad_2]
Source link



