[ad_1]
Human Useful resource Administration (HRM) is a proper system designed to supervise individuals inside a company. Its core duties embody staffing, managing worker compensation, and defining and designing work roles to make sure optimum organizational effectivity.
Human Assets Improvement (HRD) refers to uncovering and nurturing latent skills inside people in a company. This permits them to carry out new duties effectively and profit each themselves and the corporate.
| Side | HRM | HRD |
| Focus | Administration and administration. | Worker improvement and studying. |
| Purpose | Environment friendly useful resource utilization. | Improve particular person efficiency. |
| Tasks | Staffing, compensation, roles. | Expertise identification, coaching. |
| Strategy | Reactive, short-term. | Proactive, long-term funding. |
| Final result | Environment friendly workforce. | Expert, motivated workers. |
HRM offers with total personnel administration, whereas HRD particularly focuses on strategic planning to construct a profitable group. Understanding the variations between the 2 will allow companies to implement focused insurance policies and be sure that workers are managed in addition to developed.
The next explains the essential meanings and definitions of HRM and HRD whereas we perceive their key similarities and variations intimately.
What’s HRM or Human Useful resource Administration?
HRM or Human Useful resource Administration is the method of acquisition, improvement, and retention of expert workers to attain organizational goals proficiently. It focuses on the method of hiring people, nurturing their skills, and utilizing and compensating their providers.
In response to Statista, 47% of huge organizations reported having an on-premise Human Assets Administration System (HRMS) with a license.
HRM fosters the alignment of the workers’ expertise with each job and organizational wants. The primary goal of it’s to help the objectives of the group, people, and society as an entire.
Definition of HRM
The human useful resource administration refers back to the philosophy, insurance policies, procedures, & follow associated to the administration of individuals inside a company.
– Wendell L French
HRM is a course of consisting of the acquisition, improvement, motivation & upkeep of human assets.
– Stephen P Robbins
Evolution of HRM
The idea of Human Useful resource Administration (HRM) has developed by way of distinct durations. Let’s have a short take a look at it.
-
Pre-Industrial Revolution:
-
-
- Restricted crafts, apprentices assisted craftsmen.
-
-
Industrial Revolution (1750-1850):
-
-
- Shift to an industry-based economic system.
- Departments for wages, welfare, and housing have been established.
- Labor unions emerged, resulting in industrial relations departments.
-
-
-
- Frederick W. Taylor: Launched scientific administration ideas.
- Hawthorne Research: Shifted focus to employee satisfaction.
- Douglas McGregor & Abraham Maslow: Transitioned to dynamic HRM, viewing employees as useful assets.
-
-
At the moment:
-
- An integral a part of core enterprise capabilities.
- Includes recruitment, motivation, coaching, and efficiency value determinations.
-
Capabilities of HRM
The capabilities of Human Useful resource Administration may be broadly divided into managerial and operational capabilities. The actions which are included in it are as follows:
Managerial Capabilities
- Planning: Formulating methods and packages upfront to fulfill organizational objectives, together with HR necessities, choice, and coaching.
- Organizing: Structuring duties, defining relationships, and integrating actions towards frequent goals throughout the group.
- Directing: Activating workers and maximizing their contributions by way of efficient course, motivation, and tapping into their potential.
- Controlling: Monitoring and evaluating precise worker efficiency with plans, implementing management measures when deviations happen.
Operative Capabilities:
- Job Evaluation: Finding out particular job roles and duties.
- HR Planning: Guaranteeing the provision of certified personnel to fulfill organizational wants.
- Recruitment: Looking for potential workers and inspiring them to use.
- Choice: Assessing candidates’ {qualifications} and suitability for the job.
- Placement: Matching chosen candidates with appropriate job roles.
- Induction & Orientation: Serving to new workers modify to the group’s setting, insurance policies, and folks.
Latest traits within the discipline of HRM
The latest traits and developments in human useful resource administration revolve across the rising give attention to worker engagement and motivation. Corporations are persevering with their efforts to enhance work tradition to retain the perfect skills.
A survey of those traits factors towards the respective significance in percentages.
- Hybrid work mannequin: 32%
- Change administration: 18%
- Wholesome group: 15%
- Steady studying: 15%
- Flexibility: 12%
- Concentrate on worker retention: 6%
- Group primarily based on expertise: 2%
What’s HRD or Human Useful resource Improvement?
Human Useful resource Improvement (HRD) is the systematic technique of enhancing the talents and talents of particular person workers, groups, and all the group. Its purpose is to align private development with organizational goals, fostering a tradition the place teamwork and collaboration thrive.
It promotes sturdy relationships, skilled well-being, motivation, and satisfaction amongst workers, guaranteeing they contribute successfully to attaining the group’s objectives.
Definition of HRD
Nadler (1970) described HRD as structured actions aimed toward producing behavioral change inside a set timeframe. In his revised definition in 1984, he outlined HRD as organized studying experiences inside a particular interval to reinforce job efficiency and private development alternatives.
Evolution of HRD
- Early Industrial Period (Late nineteenth to Early twentieth Century):
-
-
- Concentrate on labor administration and effectivity.
- Restricted emphasis on worker improvement.
- Submit-World Warfare II Period (Nineteen Forties – Fifties):
- Rise of scientific administration ideas.
- Emergence of coaching packages for talent improvement.
-
-
-
- Shift in the direction of humanistic approaches in administration.
- Introduction of behavioral sciences to grasp human habits at work.
- Emergence of coaching and improvement as formal capabilities inside organizations.
-
- Nineteen Eighties – Nineties:
-
-
- Integration of HRD with organizational technique and planning.
- Concentrate on Whole High quality Administration (TQM) and steady enchancment.
- Introduction of ideas like organizational studying and information administration.
-
- Late Nineties – Early 2000s:
-
-
- The appearance of technology-driven studying and improvement.
- Rising emphasis on e-learning and digital coaching packages.
-
- twenty first Century (2000s – Current):
-
-
- Elevated consideration on expertise administration and succession planning.
- Growth of HRD to incorporate profession improvement, mentoring, and training.
- Integration of variety and inclusion initiatives in HRD practices.
- Rise of data-driven HRD with the usage of analytics for decision-making.
-
-
-
- Emphasis on agile and modern studying methodologies, incorporating adaptive and customized studying strategies.
- Integration of synthetic intelligence and machine studying in HRD processes for enhanced effectivity and customized talent improvement.
- Concentrate on worker well-being and psychological well being help as a part of HRD initiatives.
-
Capabilities of HRD
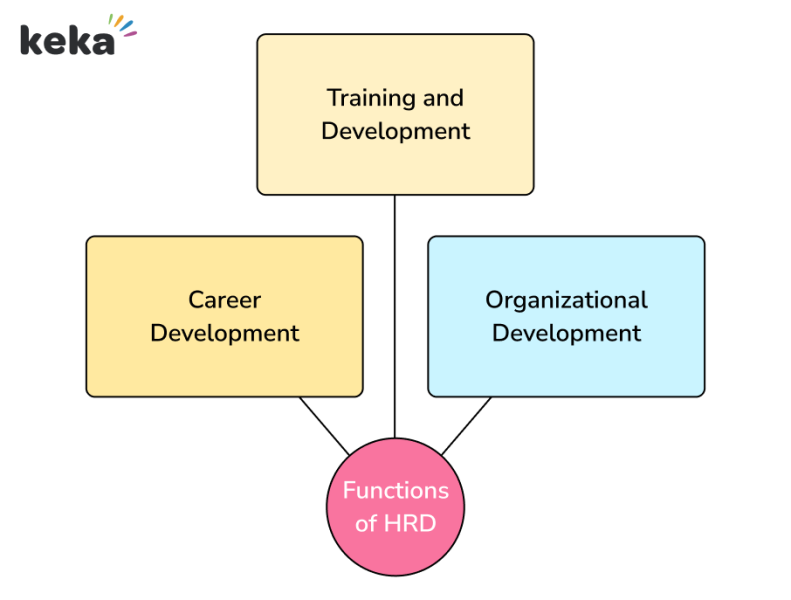
1. Coaching and Improvement (T&D)
T&D focuses on enhancing the information, expertise, and attitudes of people. Coaching includes offering workers with particular expertise wanted for duties, whereas developmental actions put together workers for future duties and improve their present capacities.
T&D actions begin with new worker orientation and expertise coaching, evolving into teaching and counseling as workers grow to be proficient. Teaching emphasizes worker duty and purpose achievement, whereas counseling addresses private points affecting work objectives.
2. Group Improvement (OD)
OD goals to reinforce organizational effectiveness and member well-being by way of deliberate interventions primarily based on behavioral science ideas. Macro modifications give attention to total organizational enchancment, whereas micro modifications goal people, small teams, and groups.
HR professionals operate like change brokers in a company. They advise and facilitate interventions, equivalent to implementing worker involvement packages to reshape work expectations, reward methods, and reporting procedures.
3. Profession Improvement
Profession improvement is an ongoing course of involving profession planning and administration. Profession planning assesses a person’s expertise and establishes a sensible profession plan, typically with counselor help.
Profession administration includes taking steps to attain the plan and specializing in what the group can do to foster worker profession improvement. Coaching packages can play a job in implementing profession plans.
Latest developments in HRD
Human Useful resource Improvement (HRD) has undergone vital transformations to maintain tempo with evolving wants. These modifications mirror the profound influence of globalization, digitalization, and shifting organizational priorities.
Listed here are some latest traits:
1. Globalization
With the rise of world markets, HRD focuses on growing cross-cultural competencies and understanding numerous work cultures to successfully handle worldwide groups and increase companies globally.
2. Strategic HRD and Expertise Administration
HRD aligns carefully with organizational methods, figuring out and nurturing key skills. Strategic planning ensures the precise expertise are developed, and expertise is managed to attain long-term enterprise objectives.
3. Digital, Cell, and Social Studying
HR improvement leverages digital platforms, cellular apps, and social media for coaching and studying initiatives. This method permits workers to entry coaching supplies wherever, anytime, fostering steady studying.
4. Administration and Management Improvement
HRD invests in packages to domesticate efficient administration and management expertise amongst workers. These initiatives give attention to enhancing decision-making skills, communication, and workforce administration expertise.
5. Efficiency Consulting
HR professionals act as efficiency consultants, analyzing organizational challenges and recommending coaching interventions. These developments are used to enhance productiveness, effectivity, and total efficiency.
6. Profession and Efficiency Administration
HRD helps workers of their profession development, offering assets for talent improvement and profession planning. It additionally integrates efficiency administration methods, guaranteeing workers’ objectives align with organizational goals.
7. Proactive Studying
Human assets improvement anticipates future talent wants and supplies proactive studying alternatives. It emphasizes staying forward of {industry} traits, enabling workers to adapt to altering job roles and applied sciences.
8. Studying Design and Construction
HRD focuses on designing participating and efficient studying experiences. This consists of structuring coaching packages, incorporating interactive parts, and using varied codecs to cater to completely different studying kinds. This ensures most information retention.
Key similarities between HRM and HRD
The important thing similarities between Human useful resource administration and human useful resource improvement have been talked about beneath.
| Function | HRM | HRD |
| Managing and nurturing the workforce |  |
 |
| Recruiting, choosing, and coaching workers |  |
 |
| Enhancing worker efficiency and productiveness |  |
 |
| Dealing with worker relations and battle decision |  |
 |
| Implementing insurance policies for authorized compliance |  |
 |
| Evaluating worker efficiency |  |
 |
| Creating profession development alternatives |  |
 |
| Adopting a long-term strategic method |  |
 |
| Using knowledge and analytics for decision-making |  |
 |
| Aligning HR practices with organizational technique |  |
 |
Key variations between HRM and HRD
Human Useful resource Administration includes making use of administration ideas to supervise the group’s workforce. Then again, Human Useful resource Improvement focuses on steady enchancment efforts to reinforce the efficiency of workers throughout the group.
The ten key variations between the 2 have been talked about beneath in response to varied features.
1. Nature
HRM operates as an important part throughout the broader administration framework, falling beneath the overarching operate of organizational administration. In distinction, HRD capabilities as a subsidiary of HRM, intricately linked to the administration of human assets however with a particular give attention to improvement and development.
2. Focus
HRM facilities its consideration on overseeing the group’s human assets, together with administrative duties, insurance policies, and procedures. It ensures the environment friendly administration of workers and addresses speedy issues throughout the organizational construction.
Conversely, HRD concentrates on the enhancement of workers’ expertise, information, and capabilities, fostering particular person and organizational development. It’s geared in the direction of constructing a proficient workforce to attain long-term success.
3. Scope
Inside HRM, duties embody recruitment, compensation structuring, managing worker relations, and guaranteeing compliance with legal guidelines and rules. Then again, HRD’s scope is broader, involving coaching packages and expertise administration initiatives. It additionally fosters a tradition of steady studying throughout the group.
4. Function
HRM’s main goal lies in aligning workers with the group’s enterprise goals, guaranteeing they’re in appropriate roles and effectively managing their day-to-day duties. In distinction, HRD focuses on enhancing particular person and organizational efficiency.
It achieves this by investing in worker studying and improvement, fostering private {and professional} development, and constructing a talented and adaptable workforce.
5. Time Horizon
HRM primarily offers with short-term objectives, addressing speedy staffing wants and short-term worker points that come up throughout the group. In distinction, HRD operates with a long-term perspective, concentrating on strategic planning and making ready workers to fulfill future challenges efficiently.
6. Orientation
Whereas HRM is geared towards guaranteeing organizational effectivity and optimum useful resource administration. In the meantime, HRD’s orientation is firmly rooted in worker development, engagement, and profession development throughout the group.
HRD actions are geared in the direction of empowering workers to attain their full potential.
7. Dependency
HRM capabilities independently, comprising varied sections equivalent to recruitment, retention, HRD, compensation, and efficiency appraisal administration. HRD operates as an integral a part of HRM, drawing capabilities, attributes, and processes from the broader HRM framework, indicating a detailed interdependence between the 2.
8. Formality
HRM capabilities are usually formal, involving structured strategies like classroom or laboratory coaching to make sure standardized implementation. In distinction, HRD capabilities may be casual, typically involving mentorship and training from superiors, notably managers. It signifies a extra customized and adaptive method to worker improvement.
9. Course of
HRM follows customary procedures, executed each time the necessity arises. In distinction, HRD processes are steady, specializing in ongoing studying and improvement initiatives. It displays a proactive and adaptive method to worker development throughout the group.
10. Precedence
Human Useful resource Administration prioritizes the general development of all the group, whereas Human Useful resource Improvement locations unique give attention to people
Right here’s a desk showcasing the variations between HRM and HRD.
| Side | HRM | HRD |
| Nature | HRM falls beneath the administration operate | HRD is a subsidiary of HRM |
| Focus | Overseeing the group’s human assets and dealing with administrative duties, insurance policies, and procedures. | Bettering workers’ expertise, information, and capabilities to foster development and organizational success. |
| Scope | Recruitment, compensation, worker relations, and compliance with legal guidelines. | Coaching, expertise administration, and fostering a studying tradition throughout the group. |
| Function | To align workers with enterprise goals, guaranteeing they’re in appropriate roles, and handle their each day duties effectively. | Enhancing particular person and organizational efficiency by investing in worker studying, fostering development, and a proficient workforce. |
| Time Horizon | Brief-term objectives speedy staffing wants and short-term worker points | Lengthy-term objectives and strategic planning, making ready workers for future challenges. |
| Orientation | Organizational effectivity and useful resource administration | Worker development, engagement, and profession development throughout the group. |
| Dependency | Operates as a definite entity, consisting of assorted sections like recruitment, retention, HRD, compensation, and efficiency appraisal administration. | A part inside HRM; incorporates capabilities, attributes, and processes from the broader HRM framework. |
| Formality | Capabilities are usually formal and carried out by way of classroom or laboratory coaching strategies. | Capabilities may be casual, involving actions like mentorships and training from superiors, typically managers. |
| Course of | Commonplace procedures that must be executed each time the necessity arises. | Processes are steady and never occasional. |
| Precedence | The general development of the group | Completely on the individuals of the group |
Transferring On
Within the years 2023 and 2024, Human Assets’ fundamental focus might be on workers, emphasizing their well-being and creating higher work environments, together with digital areas. The way forward for HR is anticipated to deliver nice surprises for workers as the following yr unfolds.
The brand new yr shall usher in traits like hybrid work fashions, digital work environments, versatile work tradition, Synthetic Intelligence, and so on much more strongly. Evidently, 74% of U.S. corporations (Zippia) are both utilizing or planning to undertake a everlasting hybrid work mannequin.
Moreover, there was plenty of give attention to well-being discrepancy. There’s a 22% (McKinsey Survey) hole between employer and worker perceptions of well-being at work, highlighting a disparity in understanding. Gaps like these should be opted out as the trendy workforce has no room for poisonous work cultures.
For instance, Worker Useful resource Teams (ERGs) for ladies, veterans, LGBTQ+ workers, individuals of colour, people with disabilities, and dealing mother and father, provide protected areas inside organizations.
The above factors to a course the place human useful resource administration and improvement are on the peak of their evolution. Therefore, HR professionals are sure to remain up to date on present and future traits.
In 2024, we are able to count on a big give attention to technological developments and a extra employee-centric method in companies. This shift goals to reinforce varied HR capabilities, guaranteeing improved effectivity and effectiveness inside organizations.
Incessantly Requested Questions
1. What’s the distinction between HRM and HRD?
HRM (Human Useful resource Administration) focuses on managing individuals inside a company and coping with administrative duties, insurance policies, and procedures. HRD (Human Useful resource Improvement) emphasizes enhancing workers’ expertise, information, and capabilities to foster development and organizational success by way of studying and improvement initiatives.
2. Which method has a short-term focus: HRM or HRD?
HRM has a extra short-term focus than HRD. It addresses speedy HR necessities and resolves present operational points which may lack long-term planning and forecasting.
3. Can HRM and HRD work collectively harmoniously?
Sure, HRM and HRD can work collectively harmoniously. HRM handles administrative duties and speedy operational wants, whereas HRD focuses on worker improvement and long-term development. When these capabilities collaborate, organizations can obtain a balanced method, guaranteeing each speedy necessities and long-term objectives are met successfully.
4. What are the advantages of integrating HRM and HRD practices?
The primary advantages of integrating HRM and HRD practices are:
- Holistic Worker Improvement: Integrating HRM and HRD ensures a complete method to speedy help and long-term talent enhancement.
- Strategic Alignment: HR practices align straight with organizational objectives, enhancing the corporate’s strategic goals.
- Improved Productiveness: Effectively-rounded improvement boosts worker expertise and engagement, resulting in elevated effectivity.
- Enhanced Expertise Retention: Investing in worker improvement fosters loyalty and reduces turnover charges.
5. How can organizations strike a steadiness between HRM and HRD?
Organizations can strike a steadiness between HRM and HRD by fostering communication and collaboration between the 2 capabilities. This may be achieved by aligning HRM’s speedy operational wants with HRD’s give attention to long-term worker improvement. Establishing clear objectives, integrating coaching packages, and selling a tradition of steady studying can harmonize HRM and HRD efforts. This ensures a balanced method to managing workers’ speedy wants and long-term development.
[ad_2]
Source link





