[ad_1]
The web is a marvel of recent expertise, connecting individuals and knowledge throughout the globe. However have you ever ever puzzled the way it really works?

On this weblog put up, we‘ll break it down into easy-to-understand phrases, in order that anyone and everyone can grasp how this invention works — and the way it’s modified the globe.

How the Web Started
Nikola Tesla launched the concept of a “world wi-fi system” within the 1900s. From there, different visionaries akin to Paul Otlet and Vannevar Bush started to construct on the concept Nineteen Thirties and Nineteen Forties, with plans of searchable media databases that performed as stepping stones paving the way in which to the trendy web.
M.I.T. scientist J.C.R. Licklider got here up with an answer in 1962: an “intergalactic laptop community” that may enable for communication on a worldwide scale.
What Licklider described would ultimately change into the trendy web. Nonetheless, with a view to make it occur, scientists would first must provide you with a brand new expertise: packet switching.
Now, let’s dive deeper into how knowledge is transmitted over the web.
Circuit Switching and Packet Switching
There are two fundamental strategies to how we transport knowledge: circuit switching and packet switching. Circuit switching is corresponding to taking a practice. Knowledge is shipped in a steady connection, very like passengers touring collectively in a practice carriage.
Alternatively, packet switching is akin to automobiles on a freeway. Knowledge is split into smaller chunks referred to as packets, which might take completely different routes to succeed in their vacation spot. This flexibility permits for extra environment friendly and dependable knowledge transmission.
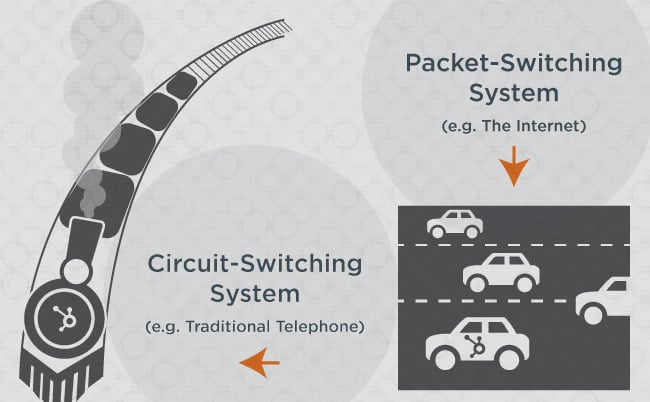
However circuit and packet switching aren‘t the one means that knowledge is shared, as a result of similar to in actual life, these modes of transportation can’t intersect, and might expertise too excessive visitors (knowledge packets) on the identical freeway (channel) to work correctly — and will ultimately come to a halt.
By the early Seventies, ARPA’s packet-switching laptop community (the imaginatively named “ARPAnet”) was rising and connecting with different packet-switching laptop networks around the globe.
However there was one drawback: Computer systems working on all of those disparate laptop networks couldn‘t talk instantly with each other. There wasn’t a single, worldwide web. As an alternative, there have been a bunch of mini-internets.
To unravel this drawback, laptop scientists developed the Transmission Management Protocol (TCP) and the Web Protocol (IP).
The Introduction of TCP/IP
TCP is liable for dividing knowledge into packets at one finish of a transmission and reassembling these packets on the different finish.
IP, compared, is liable for the formatting and addressing of the info packets being despatched. That‘s why every host laptop on the web wants an IP tackle: a novel, numerical label that distinguishes one host from one other. With out IP addresses, knowledge packets wouldn’t be capable of get to their correct locations.
When applied collectively, TCP/IP is the communication language of the web, and it was the important thing to creating the web a really worldwide community.
Trendy TCP/IP networks use 4 distinct layers with a view to transmit knowledge, and that knowledge at all times strikes from one layer to the subsequent.
- The applying layer: liable for interfacing with laptop functions akin to net browsers and electronic mail shoppers.
- The transport layer: the place the Transmission Management Protocol (TCP) goes to work dividing knowledge into packets (and, on the receiving finish, it reassembles that knowledge).
- The web layer: the place the Web Protocol (IP) assigns tackle data and determines the route the info will take.
- The community layer: bodily {hardware} really carries the info by way of wire, fiber, radio and so on.
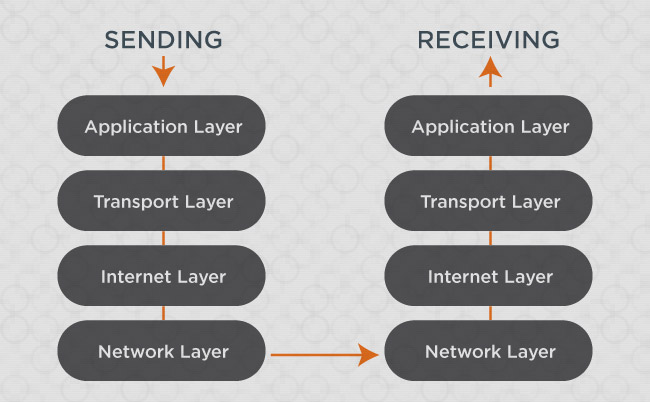
And to make sure we’re all on the identical web page right here, let me make this fast simile: Sending knowledge throughout a TCP/IP community is like sending a letter by means of the mail by way of the postal service.
- Within the software layer, you‘re writing the precise letter that you simply’re going to ship.
- Within the transport layer, you are packaging that letter in an envelope.
- Within the web layer, you are writing the tackle of the recipient on the envelope, in addition to your return tackle.
- And at last, within the community layer, you are placing the letter within the mail so postal staff can ship it.
The TCP/IP breakthrough within the ‘70s meant that scientists within the ’80s obtained to have a ton of enjoyable sending knowledge to one another throughout a really international community. Nonetheless, there was nonetheless a giant piece lacking from the trendy web we all know and love at the moment: the World Vast Net.
How the World Vast Net Got here to Be
Up till the ’90s, there have been no web sites, and no World Vast Net to gather them. That each one modified with software program engineer Tim Berners-Lee, who first proposed the idea of a World Vast Net in 1989. By the tip of 1990, he had efficiently launched the primary net web page.
Berners-Lee was on a mission to create a extra helpful web — an web that wasn’t merely a community for sending and receiving knowledge, however a “net” of knowledge that anybody on the web may retrieve. With a purpose to accomplish this, he wanted to develop three important items of expertise, that are:
- HyperText Markup Language (HTML): That is the usual protocol for publishing content material on the internet. It is used to format textual content and multimedia paperwork in addition to hyperlink between paperwork.
- Uniform Useful resource Identifier (URI): Similar to each laptop on the web will get a novel identifier within the type of an IP tackle, each useful resource on the World Vast Net will get a novel identifier within the type of a URI. The commonest sort of URI is the Uniform Useful resource Locator, or URL (also called a “net tackle”).
- HyperText Switch Protocol (HTTP): HTTP is liable for requesting and transmitting net pages. If you enter a URL into an online browser, you are really initiating a HTTP command to go discover and retrieve the online web page specified by that URL. In relation to a TCP/IP community, HTTP is a part of the applying layer, as particular functions — particularly, net browsers and net servers — use HTTP to speak with each other.
The World Vast Net as Berners-Lee noticed is what we’re utilizing, connecting, and studying from to today. And it is smart how we’re in a position to search for and discover the knowledge we’re searching for — simply consider the web like a library of robots.
How the Web Works Easy Clarification
The web, or the World Vast Net, works as an enormous library with pleasant robots. Every e-book on this library represents an online web page, they usually all observe a particular format, which is HTML. When you realize the decision quantity, or the URI, a useful robotic, which represents the HTTP protocol, retrieves the e-book for you. And if you do not know the precise name quantity, search engines like google and yahoo like Google can help you to find the knowledge you are searching for.
Web = Understood
In order that‘s how the web works. Simply keep in mind that that is simply scratching the floor. In case you’re wanting to delve deeper into the intricacies of the web, our pleasant robotic, Google, is at all times there to help you with extra data.
By understanding the basics of the web and its applied sciences, you’ll be able to achieve a better appreciation for the facility and potential that lies inside this unbelievable device.

Editor’s notice: This put up was initially printed in October 2014 and has since been up to date for comprehensiveness.
[ad_2]
Source link



